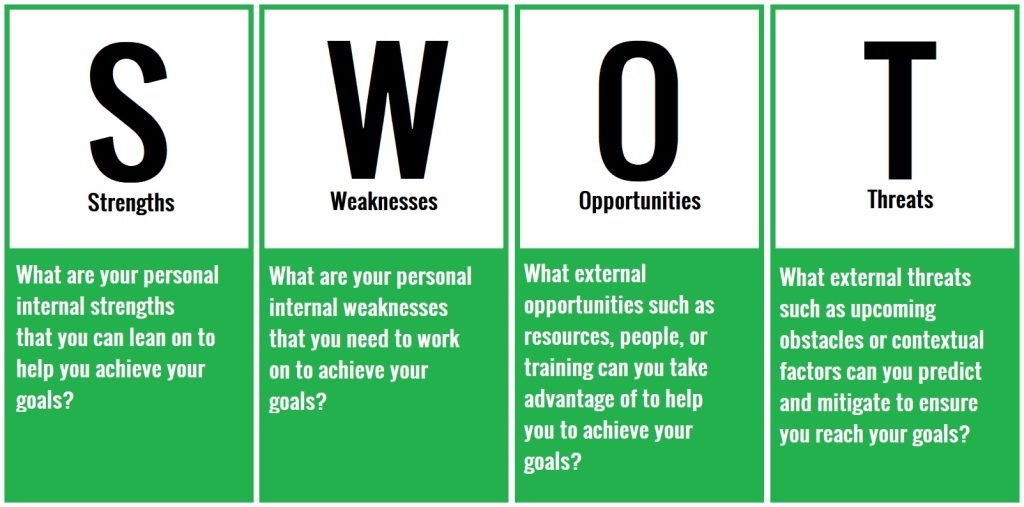
What is SWOT Analysis? SWOT analysis definition
Contents
- 1 What is SWOT Analysis? SWOT analysis definition
- 2 SWOT Analysis Analysis to Understand
- 3 The components of SWOT Analysis
- 4 SWOT analysis Table
- 5 How to do a SWOT analysis?
- 6 Advantages of SWOT Analysis
- 7 SWOT Analysis Example
- 8 SWOT Analysis Template
- 9 What is SWOT Analysis?
- 10 What is an example from SWOT Analysis?
- 11 What are the four Steps in SWOT analysis?
- 12 How do you write a Great SWOT Analysis?
- 13 Why is SWOT Analysis used?
- 14 Last word
what is SWOT analysis? what is swot analysis and examples? how to do a swot analysis? what is swot analysis and examples?
SWOT (strengths, weaknesses potentials, strengths, and threats) analysis provides a model that is used to assess strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats business’s competitiveness and also to formulate strategic plans. SWOT analysis evaluates both external and internal factors in addition to current and potential future threats.
SWOT analysis was designed to provide a real-world facts-based, data-driven glance of the advantages and weaknesses of an initiative, organization, or even within the industry. It is essential for the organization to keep the analysis up-to-date by avoiding preconceived notions or grey areas, and instead focusing on actual situations. The company should make use of the data as a guide, but not necessarily as a guideline.
important Takeaways
- SWOT analysis is an effective plan technique that gives evaluation tools.
- The identification of the core strengths, weaknesses as well as threats, opportunities, and weaknesses can lead to an analysis based on facts, new perspectives, and innovative concepts.
- A SWOT analysis combines information that comes from internal sources (strengths or weaknesses of a particular business) in addition to external forces that can impact decisions that are uncontrollable (opportunities or threats).
- SWOT analysis is most effective when diverse voices or groups within an organization are able to share real-world information rather than prescriptive communications.
- The results of a SWOT analysis are usually synthesized to aid in a single goal or decision a business faces.
SWOT Analysis Analysis to Understand
A SWOT analysis can be described as a strategy to evaluate the performance, competitiveness risks, and potential of a business and also as a business itself, like a division or product line or industry, or other organization.
Utilizing information from both sources The technique can help businesses choose strategies that are more likely to succeed and away from ones that have proven to be or are likely to be less successful. The independent SWOT analyst, investor, or even competitors can help them determine if an organization’s product line, product line, or even industry is good or weak, and what the reason is.
The components of SWOT Analysis
Every SWOT analysis should include these four types of categories. While the details and results within these categories may differ between companies the SWOT analysis will not be complete without all of the following elements:
Strengths in SWOT analysis
Strengths are the things an organization is good at and what distinguishes it from competitors with a solid brand, a loyal client base, a solid balance sheet, exclusive technology, and so on. For instance, the hedge fund might have developed a unique trading strategy that yields market-beating returns. The fund must decide on which strategy to apply the results to draw in new investors.
Example of Strengths in SWOT Analysis
-
What is the marketing mix of the company?
-
What is the USP of the company?
-
What is the market share of the company?
-
How is the management of the company?
-
Is the industry demand increasing or decreasing?
-
How is the marketing effort of the company?
-
What are the brand value and brand equity of the company?
-
Examples of Strengths – brand equity, distribution, innovation, and customer loyalty.
The weaknesses in SWOT analysis
The weaknesses of an organization prevent it from operating at its highest level. These are areas where the company must improve to stay competitive. Examples include an unprofessional brand, higher-than-average turnover and high amounts of debt, an insufficient supply chain, or lack of capital.
Example of Weaknesses in SWOT Analysis
-
Is the company utilizing resources optimally?
-
How are the financials of the company?
-
Is the company losing out to the competition?
-
How is the channel strength of the company?
-
How is the loyalty of stakeholders including internal and external customers?
-
How is the organizational culture?
-
Losing brand equity or too much competition?
Opportunities in SWOT analysis
Opportunities are external factors that are favorable to an organization and could give an organization a competitive advantage. For instance, if a country reduces the tariffs on cars, car manufacturers could sell their vehicles to the market of a different country, increasing the number of sales as well as the market’s share.
Example of Opportunities in SWOT Analysis
- Is any innovation possible?
- Left out markets and geographical territories?
- Any niche markets to be covered?
- The new technology can be applied to improve the top line or bottom line?
- Developing mutually beneficial partnerships?
- Acquiring or merging with a similar product/company?
- Product line extensions?
Threats in SWOT analysis
Threats are those that pose the potential to damage a business. For instance, a drought can be a risk to any wheat-producing business since it can cause damage or a decrease in the crop’s yield. Other threats that are common include things like rising prices for materials, increased competition, and a tight supply of labor. and so on.
Example of Threats in SWOT Analysis
- Increase in competition
- Changes in pricing
- Rising Bottomline and dropping topline
- Credit control
- Outdated technologies
- Poor cost control
- Ineffective processes
- Political and environmental influence?
SWOT analysis Table
Analysts offer a SWOT analysis in the form of an elongated square divided into four quadrants, each devoted to an aspect of SWOT. This arrangement of visuals provides an overview of the company’s position. While all the aspects under one heading might not be equally important but they should all provide important information regarding the relationship between potential threats and opportunities, the strengths and weaknesses, etc.
It is the SWOT table is typically constructed with the internal factors in the top row and external factors in the lowest row. Additionally, the elements on the left of the table are considered to be more favorable or positive, while those on the right have more concerning or negative elements.
How to do a SWOT analysis?
A SWOT analysis could be broken down into several actions with actionable items prior to and after the analysis of the four parts. In general, the SWOT analysis involves some of the steps below.
Step 1: Determine Your Objective.
An analysis of SWOT can be broad, however, the most value is likely to be produced if the analysis is focused on a specific objective. For instance, the purpose of a SWOT analysis could be focused solely on the decision to undertake an item release. With a goal in mind, a business will be able to determine the goals they intend to reach the conclusion of this process. In this instance, the SWOT analysis will help to determine what product is suitable to be made available for sale.
Step 2. Gather the resources.
Each SWOT analysis will differ and companies might require different data sets to allow for the blending of different SWOT table analyses. The company must start by understanding the data they have access to, the data limitations it has to face and the reliability of the sources of data it gets from outside.
In addition to the data, an organization must also know the best combination of staff that should be included in the process of analysis. Certain employees may be more closely connected to external forces, and other personnel from those in the department of manufacturing and the sales departments might be more aware of what’s happening within the company. Being able to see a wide range of views is more likely to produce different, valuable contributions.
Step 3. Compile Ideas.
For each of the four parts of the SWOT analysis, the team responsible for the analysis should first list suggestions within each category. Some examples of questions to think about or ask for each group are listed in the table below.
SWOT analysis Internal Factors
What happens within the business is a good source of data for how to assess the strengths as well as the weaknesses sections in the SWOT assessment. Examples of internal elements comprise financial, human resources physical, and intangible (brand) assets, as well as operational efficiency.
The possible questions to include in internal variables include:
- (Strength) What do we do well?
- (Strength) (Strength) What is our most valuable asset?
- (Weakness) What are our biggest critics?
- (Weakness) Which are the product lines that perform poorly?
SWOT analysis External Factors
Outside of the organization is just important to the overall performance of a business as internal influences. External influences, like the monetary policy and market fluctuations as well as access to suppliers, are a few categories that can be analyzed to come up with a list of possibilities and weaknesses.1
Possible questions to consider putting on the list of external variables include:
- (Opportunity) (Opportunity) apparent in the market?
- (Opportunity) Which demographics aren’t we targeting?
- (Threat) (Threat) is there (Threat) How many competitors are there, as well as what percentage of their share is?
- (Threat) Are there any new regulations that could impact our products or operations?
Strengths
1. What is our competitive edge?
2. What are the resources we have?
3. Which products are performing best?
Insufficiencies
1. What can we do to be improved?
2. What are the products that aren’t performing?
3. What are the areas where we’re lacking resources?
Opportunities
1. What is the latest technology we can utilize?
2. Are we able to expand our operations?
3. What are the new segments we can try?
Threats
1. What are the new regulations?
2. What do competitors are doing?
3. What are the trends in consumer behavior?
The company could consider conducting this process as a “white-boarding” (or “sticky notes” session. The idea is that there is no correct or incorrect answer, and all participants are allowed to share any thoughts they might have. They can then be rejected, but it is important to think of the most diverse ideas to spark creativity and inspire others.
Step 4: Review Findings.
After having a list of thoughts in each category, it’s time to refine the thoughts. After redefining the thoughts everyone thought of, companies can narrow its focus to only the most effective ideas or biggest threats to the company. This phase could require a lot of discussions among the analysis participants as well as bringing in higher management to help prioritize the priorities.
Step 5: Design the Strategy.
Armed with the list of ranked strengths as well as weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, it’s time to transform your SWOT analysis into the form of a strategic plan. Analysis team members examine the bulleted list of things within each category and develop an organized plan that offers guidelines on the initial goal.
For instance, a business contemplating whether to release an entirely new product could have been discovered as the leader in the market for its current product, and there is a possibility of expanding to new markets. However, higher costs for materials and strained distribution lines the requirement for staffing, and unpredictable demand for the product demand could outweigh the advantages and potential. The team of analysts develops the plan to review the decision within six months with hopes that costs will decrease and demand being more transparent.
Tips: Make use of SWOT analysis to pinpoint issues that impact your business and opportunities to improve it. But, remember that it is just one of the many strategies but not a definitive plan.
Advantages of SWOT Analysis
The SWOT analysis isn’t going to answer all the major questions a company faces. There are a variety of advantages to an analysis of SWOT that makes strategic decision-making much easier.
- The SWOT Analysis helps make difficult problems easier to manage. There may be an inordinate amount of information to review and pertinent aspects to be considered when making a difficult decision. In general, the case of a SWOT analysis made by breaking down the ideas into bullets and ranked in order of importance will distill an overwhelming, possibly overwhelming issue into an accessible report.
- SWOT analysis needs external consideration. In many cases, companies might be enticed to only look at internal aspects in making decisions. However, there are a lot of factors beyond the company’s control that could impact the outcomes of a business choice. A SWOT analysis will cover both the internal elements the company is able to control as well as external elements that might be more difficult to manage.
- A SWOT analysis is used to answer almost any business issue. The analysis could be applied to an entire team, organization, or even an individual. It also can examine a complete range of product or brand changes and geographical expansion or acquisition. It is possible to analyze the SWOT assessment as a flexible instrument that can be used for a variety of purposes.
- A SWOT assessment makes use of various sources of data. A company will likely use internal data to identify its strengths as well as weaknesses. It will also have to obtain external data related to the broad market, competitors, and macroeconomic forces to identify potential threats and opportunities. Instead of relying solely on one possibly biased source, a thorough SWOT analysis combines different perspectives.
- SWOT analysis might not cost a lot to create. Some SWOT reports don’t require a lot of technical. Therefore, several staff members are able to help in the preparation of it without formal training or consulting from outside.
SWOT Analysis Example
In 2015 the year 2015, a Value Line SWOT analysis of The Coca-Cola Company noted strengths such as its worldwide recognizable brand name, its extensive distribution network, as well as opportunities in new markets. However, it also identified the weaknesses and threats, including fluctuations in foreign currency, rising public demand for “healthy” drinks, and competition from healthier beverage providers.2
Its SWOT analysis led Value Line to pose some hard questions about Coca-Cola’s strategies however, it also pointed out that Coca-Cola “will likely remain a top-tier beverage company” that could provide investors with a conservative outlook and “a steady source of income as well as some risk of capital gain exposure.”
Five years after the analysis was completed five years later, five years later, the Value Line SWOT analysis proved efficient in the sense that Coca-Cola remains the sixth strongest brand worldwide (as it was in the year). The shares of Coca-Cola (traded under the ticker symbol KO) have appreciated in value by 60% over the course of five years following the time the analysis was finished.
Understand the full picture of a SWOT analysis
To understand the full picture of a SWOT analysis, take the hypothetical scenario of an organic smoothie business. To understand better how it is competing in the market for smoothies and what it could achieve, it carried out SWOT analyses. In this study, it discovered its strengths as being a good source of ingredients, personalized services to customers, as well as a good relationship with its suppliers. Looking at its operations, it discovered several areas of weakness: limited diversification of products as well as high turnover rates and old equipment.
Analyzing how the external environment impacts its business, it found potential in new technologies and demographics that have not been explored as well as an increase in the number of people who are embracing healthy living. Additionally, it identified threats, for example, a winter freeze that can damage crops as well as a global pandemic and problems in the supply chain. Together with other strategies for planning company applied SWOT analysis to use SWOT analysis to capitalize on its strengths and opportunities externally to reduce threats and build up areas in which it was weak.
SWOT Analysis Template
Here is a SWOT analysis template in Excel format. All you have to do is utilize the SWOT template to fill in the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats!
What is SWOT Analysis?
SWOT (strengths and weaknesses-threats, opportunities, and strengths) analyses are a strategy to analyze and identify strengths and weaknesses within the organization as well as threats and opportunities from the outside that influence the current and future operation and aid in setting strategic goals. SWOT analysis is not restricted to businesses. Individuals can use SWOT analysis to gain insight into their own lives and formulate personal goals for improvement.
What is an example from SWOT Analysis?
Home Depot conducted a SWOT analysis and created an unbalanced listing of its own strengths and drawbacks, as well as external influences which could be a threat to its position in the market as well as its growth plan. Quality customer service, good brand recognition, and good relationships with suppliers were among its strengths. However its supply chain is a tangled one as well as a dependence on its U.S. market, and the ability to replicate its business model were identified as shortcomings.
In close proximity to the weaknesses of Home Depot, its dangers were similar competitors, readily available alternatives as well as the state that its position in the U.S. market. The study found and other studies the need to expand its supply chain as well as its global expansion would be crucial to its growth.3
What are the four Steps in SWOT analysis?
The four stages of SWOT analysis form the acronym SWOT strengths potential, weaknesses, and threats. These four components are broken down into two phases of analysis. A company first evaluates its own capabilities internally and evaluates its strengths and weaknesses. Then, the company is looking outward and analyzes external factors that affect the business. External factors can create opportunities or even undermine the current operations.
How do you write a Great SWOT Analysis?
The process of creating a SWOT analysis is about analyzing and identifying the strengths as well as weaknesses, opportunities, and threats facing a company. It is suggested to start by making an inventory of questions to respond to for each component. These questions are guidelines for your SWOT analysis and forming an appropriate list. The SWOT framework can be built in a list format, in free text, or more commonly in a four-cell table with quadrants devoted to each aspect. Weaknesses, as well as strengths, are first listed before potential threats and opportunities.
Why is SWOT Analysis used?
SWOT analysis is utilized to determine areas for improvements or opportunities for competitive advantage for a business. Apart from analyzing things that companies do effectively, SWOT will take into consideration the negative aspects of a company. By using this data an organization will be able to make better choices to keep doing its strengths and make the most of its strengths, reduce the risk of the weaknesses of its business, and plan for the possibility of events that could negatively influence the business in the near future.
Last word
An analysis of SWOT is the ideal way to steer meetings on business strategy. It’s a powerful idea to let all participants discuss the company’s strengths and weaknesses, determine the threats and opportunities, and come up with ideas. Sometimes, the SWOT analysis you imagine prior to the session shifts throughout to include factors that you didn’t know about and wouldn’t have been able to capture without the input of the group.
A company may use SWOTs for general business strategy meetings or to focus on particular segments like production, marketing, or sales. This way, you’ll be able to observe the way in which the overall strategy formulated through a SWOT analysis will be filtered down to the sub-sectors below before taking a decision. You could also do the reverse by using a segment-specific SWOT analysis, which is integrated into a larger SWOT analysis.
Although it can be a useful tool to plan, however, SWOT does have its drawbacks. It is just one of the strategies for business planning and shouldn’t be used on its own. Additionally, each item in these categories is not ranked the same way. SWOT is not able to reflect the variations in weight. Thus, a deeper analysis is required, employing an alternative method of planning.